
X-Ray Diffraction ( XRD)
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) is a non-destructive technique for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of crystalline materials in the form of powder or solid.
GNR in cooperation with academic and industrial users has developed a set of technically advanced and flexible X-Ray diffractometers able to satisfy the different level of requirements and different operating budget. XRD analyzer for all budgets and applications.
How X-Ray Diffractometer works …
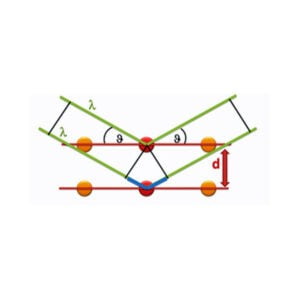
Diffraction is obtained as the “reflection” of an X-ray beam from a family of parallel and equally spaced atomic planes, following Bragg’s law: when a monochromatic X-ray beam with wavelength l is incident on lattice planes with an angle q, diffraction occurs if the path of rays reflected by successive planes (with distanced) is a multiple of the wavelength.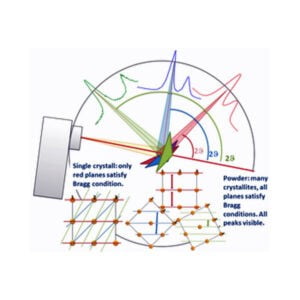
Qualitative analysis (phase analysis) can be done through the comparison of the diffractogram obtained from the specimen with a huge number of patterns included in the official databases. Single phases and/or mixtures of phases can be analysed with the programs available today.
Applications of X-Ray Diffractometer
Many Investigations can be performed with the help of X-ray diffraction.
Residual Stress forces that results in a small compression or dilatation of the d-spacing. With XRD analyzers it is possible to measure the strain (the deformation of the original lattice) and the stress is calculated based on the elastic constants of the material
The texture is the preferred orientation of the crystallites in a specimen. If a texture in a material is present, the intensity of a diffraction line changes with the orientation of the sample with respect to the incident beam.
Crystallite size and MicroStrain information are obtained by the analysis of the width and the shape of the diffraction lines.
Structure Analysis XRD is used to investigate the crystallographic structure of a material. The position and the relative intensities of the diffraction lines can be correlated to the position of the atoms in the unit cell and its dimensions. Indexing, structure refinement and simulation can be obtained with specific computer programs.
Thin-film Keeping the incident beam at low angles, it is possible to investigate the properties of multilayers by minimizing the interference of the substrate. Reflectometry can also be performed in the same way.
GNR XRD analyzer portfolio covers a huge range of applications for materials characterization and quality control of crystalline or non-crystalline materials such as powders, specimens, thin films or liquids.
XRD Analyzers
-

Portable Residual Stress Analyzer SpiderX Edge
-

Explorer – High resolution Theta Theta XRD
-

StressX – X-Ray Diffractometer for Residual Stress Measurement
-

APD 2000 PRO for Phase and Structural analysis of Powder Samples
-

Europe 600 Benchtop X-Ray Diffractometer
-

AreX L for fast and accurate Retained Austenite Measurement
-

Benchtop Retained Austenite Analyzer- Arex-D














